前言
学习树的过程中,时常需要用手画树来帮助理解,但是在编程过程中如果需要调试,树结构想要可视化比较麻烦,需要一个节点一个节点看,而网上又找到好用的可视化方案,所以自己做了个N叉树的可视化工具。如果不感兴趣原理和实现过程可以直接跳到代码实现和使用部分。
友情链接
N叉树的可视化
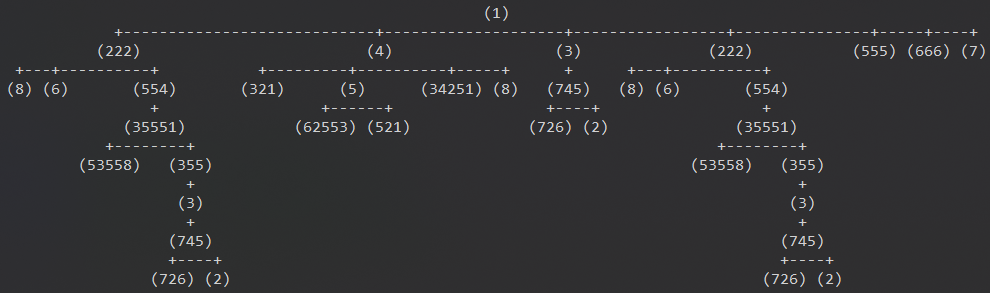
我们手工构造一个树的可视化:
(020)
+--------------+-----------------+
(070) (080) (000)
+-----+-----+ + +-----+-----+-----+
(000) (070) (020) (012) (060) (090) (012) (070)
+ +-----+
(090) (013) (014)
对其进行分析:

一个树占多大空间,取决于其子树占多大空间,子树所占的空间又可以这样递归下去,直到叶子节点。(本例中叶子节点占5个字符长度)
触底之后自底向上累加所占空间到父节点中,从而计算出该棵子树所占空间。(上图中,大方框是由小方框所确定的,理解自底向上的过程,可以自己动手画一个树,从手画的过程理解)
在这过程中,我们需要记录节点所占的空间,这里用数组length来表示,与各个子节点的所占空间一一对应,于是我们可以设计出如下数据结构。
typedef struct GraphNode{
vector<GraphNode*> child;
vector<int> length;
string content;
}*GraphTree;
具体流程如下:
- 深度优先搜索(达到叶子节点之后回溯,将所占空间传递给父节点)
- 如果叶节点,计算其内容所占空间
- 如果非叶节点,所占空间为子节点所占空间的和
代码实现如下:
void calLength(GraphTree root){
for(int i = 0; i < root->child.size(); i++){
if(root->child[i]->child.size() > 0){
calLength(root->child[i]);
//由于子树间有一个`-`进行隔断,所以起始值为子节点数-1
int sum = root->child[i]->child.size() - 1;
for(int j = 0; j < root->child[i]->child.size(); j++){
sum += root->child[i]->length[j];
}
root->length[i] = sum;
}else{
root->length[i] = root->child[i]->content.size() + 2;
}
}
}
计算完树的各子树所占空间后,就到了对其绘制的过程。但这部分并不容易,我们计算树所占空间时是垂直的,而绘制树的过程是水平的,这就带来了一定麻烦。
当我们绘制某个节点时,还需要知道其他节点所占的空间,才能确定绘制在什么位置,所以我们引入一个变量pos用来记录该节点的起始横坐标。
所以数据结构修改如下:
typedef struct GraphNode{
vector<GraphNode*> child;
vector<int> length;
string content;
int pos;
}*GraphTree;
并引入计算pos的核心函数:
void calPosition(GraphTree root){
int pos = root->pos;
for(int i = 0; i < root->child.size(); i++){
root->child[i]->pos = pos;
calPosition(root->child[i]);
//计入隔断所占的空间
pos += root->length[i] + 1;
}
}
对于一层节点,我们需要绘制两行字符串,一行表示节点值,另一行用于绘制辅助线,这里分为drawNode和drawLine。
代码如下:
string drawNode(GraphNode* node){
//计入隔断所占的空间
int length = node->child.size() - 1;
for(int segment : node->length){
length += segment;
}
//节点信息所占空间为offset*2
int offset = node->content.size() / 2 + 1;
string blank;
if(length / 2 - offset > 0){
blank += string(length / 2 - offset, ' ');
}
return blank + "(" + node->content + ")" + blank;
}
string drawLine(GraphNode* node){
string line;
//只有一个子节点时需要特殊处理
if(node->child.size() == 1){
string blank(node->length[0] / 2, ' ');
line += blank + '+' + blank;
return line;
}
for(int i = 0; i < node->length.size(); i++){
int length = node->length[i];
//起始节点和尾节点需要特殊处理
if(i == 0){
string blank(length / 2, ' ');
string segment(length / 2 + 1, '-');
line += blank + '+' + segment;
}else if(i == node->length.size() - 1){
string blank(length / 2, ' ');
string segment(length / 2, '-');
line += segment + '+' + blank;
}else{
string segment(length / 2, '-');
line += segment + '+' + segment + '-';
}
}
return line;
}
最后,我们需要根据pos进行横坐标的修正,例如下图,框内的空格,需要根据pos进行输出。
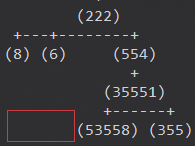
//row1代表节点信息行,row2代表辅助线行
string fix1, fix2;
if(row1.size() < node->pos){
fix1 = string(node->pos - row1.size(), ' ');
}
if(row2.size() < node->pos){
fix2 = string(node->pos - row2.size(), ' ');
}
nodeInfo = fix1 + nodeInfo;
line = fix2 + line;
代码实现
typedef struct GraphNode{
vector<GraphNode*> child;
vector<int> length;
string content;
int pos;
}*GraphTree;
void calLength(GraphTree root){
for(int i = 0; i < root->child.size(); i++){
if(root->child[i]->child.size() > 0){
calLength(root->child[i]);
//由于子树间有一个`-`进行隔断,所以起始值为子节点数-1
int sum = root->child[i]->child.size() - 1;
for(int j = 0; j < root->child[i]->child.size(); j++){
sum += root->child[i]->length[j];
}
root->length[i] = sum;
}else{
root->length[i] = root->child[i]->content.size() + 2;
}
}
}
void calPosition(GraphTree root){
int pos = root->pos;
for(int i = 0; i < root->child.size(); i++){
root->child[i]->pos = pos;
calPosition(root->child[i]);
//计入隔断所占的空间
pos += root->length[i] + 1;
}
}
string drawNode(GraphNode* node){
//计入隔断所占的空间
int length = node->child.size() - 1;
for(int segment : node->length){
length += segment;
}
//节点信息所占空间为offset*2
int offset = node->content.size() / 2 + 1;
string blank;
if(length / 2 - offset > 0){
blank += string(length / 2 - offset, ' ');
}
return blank + "(" + node->content + ")" + blank;
}
string drawLine(GraphNode* node){
string line;
//只有一个子节点时需要特殊处理
if(node->child.size() == 1){
string blank(node->length[0] / 2, ' ');
line += blank + '+' + blank;
return line;
}
for(int i = 0; i < node->length.size(); i++){
int length = node->length[i];
//起始节点和尾节点需要特殊处理
if(i == 0){
string blank(length / 2, ' ');
string segment(length / 2 + 1, '-');
line += blank + '+' + segment;
}else if(i == node->length.size() - 1){
string blank(length / 2, ' ');
string segment(length / 2, '-');
line += segment + '+' + blank;
}else{
string segment(length / 2, '-');
line += segment + '+' + segment + '-';
}
}
return line;
}
string drawGraphTree(GraphTree root){
calLength(root);
calPosition(root);
//层序遍历
vector<GraphNode*> level{root};
string graphTree;
while(level.size() > 0){
string row1, row2;
vector<GraphNode*> nextLevel;
for(GraphNode* node : level){
string nodeInfo = drawNode(node);
string line = drawLine(node);
//修正空格
string fix1, fix2;
if(row1.size() < node->pos){
fix1 = string(node->pos - row1.size(), ' ');
}
if(row2.size() < node->pos){
fix2 = string(node->pos - row2.size(), ' ');
}
nodeInfo = fix1 + nodeInfo;
line = fix2 + line;
for(GraphNode* child : node->child)
nextLevel.push_back(child);
row1 += nodeInfo;
row2 += line;
}
level = nextLevel;
row1 += '\n';
row2 += '\n';
graphTree += row1 + row2;
}
return graphTree;
}
关于使用
因为数据结构每个人都有不一样的定义,所以需要你自己构建一个可视化树,如下是一个简单的构建方法。
typedef struct Node{
vector<Node*> child;
int val;
}*NodeTree;
GraphTree constructGraphTree(NodeTree root){
int childNum = root->child.size();
GraphTree result = new GraphNode{vector<GraphNode*>(childNum)
, vector<int>(childNum)
, to_string(root->val)};
for(int i = 0; i < childNum; i++){
result->child[i] = constructGraphTree(root->child[i]);
}
return result;
}
另外,graphNode中的content长度需要是奇数,因为奇数有中心字符,而偶数没有中心字符,不对称会导致错位。
输出示例,一个比较复杂的树也能做到比较好的可视化